The importance of onshoring manufacturing in the U.S. should not be overlooked. It offers the potential to revive sectors of the U.S. economy, bring back jobs, and reclaim resources. Automation plays a key role in driving this movement, revitalizing sectors impacted by offshoring. By leveraging automation technologies, companies can optimize operations, streamline production, and boost efficiency. The integration of automation and onshoring strategies creates a sustainable and robust manufacturing ecosystem in the U.S.
Automation: Empowering Onshoring for Enhanced Manufacturing Efficiency and Competitiveness
Many U.S. companies are integrating automation into their operational processes to enhance efficiency without sacrificing job opportunities. Automation, particularly in warehouse operations, reduces costs and maximizes productivity. Despite historical challenges in implementing automation, advances in modern manufacturing technology have enabled its adoption. This includes automating tedious and hazardous tasks, driving a 10.28% increase in industrial robot installations since 2008. U.S. manufacturers’ investment of approximately $2 billion in robotics in 2021 reflects the recognition of cost reduction and process optimization for survival.
Integrating robotics and automation allows companies to allocate value-added roles to humans while automating repetitive tasks. This coexistence optimizes facility operations, leading to increased profit margins and reduced wasted time. For example, in Tesla’s Fremont factory, robots install battery packs in the cars, relieving humans of the most labor-intensive operations in the factory and reducing installation time from four to two minutes. Moreover, automation enhances the competitiveness of U.S. manufacturers by enabling effective responses to market demands, improving supply chain resilience, and adapting to consumer preferences. Embracing automation empowers businesses to achieve cost reduction, increased productivity, and enhanced competitiveness, ultimately shaping the evolving landscape of modern manufacturing and supporting the onshoring movement.
Understanding Offshoring and Its Drivers
To understand why companies based in the U.S. are choosing to relocate their manufacturing back to North America, it’s crucial to recognize why businesses initially turned to overseas manufacturing. These companies started offshoring their manufacturing to countries where production costs were significantly lower compared to the U.S. In addition to lower wages, offshoring allowed companies to avoid environmental regulations, reduce operational costs, access a larger workforce, and benefit from tax breaks offered by certain countries. Offshore manufacturing gained popularity in the 1960s and 1970s and expanded rapidly in the 1980s. This business model led to the development of entire teams dedicated to facilitating offshoring. It’s important to note that while this discussion focuses on manufacturing locations and relocation, offshoring is not limited to manufacturing work, and many companies have decentralized their workforce worldwide.
Onshoring’s Benefits: Job Creation and Economic Growth
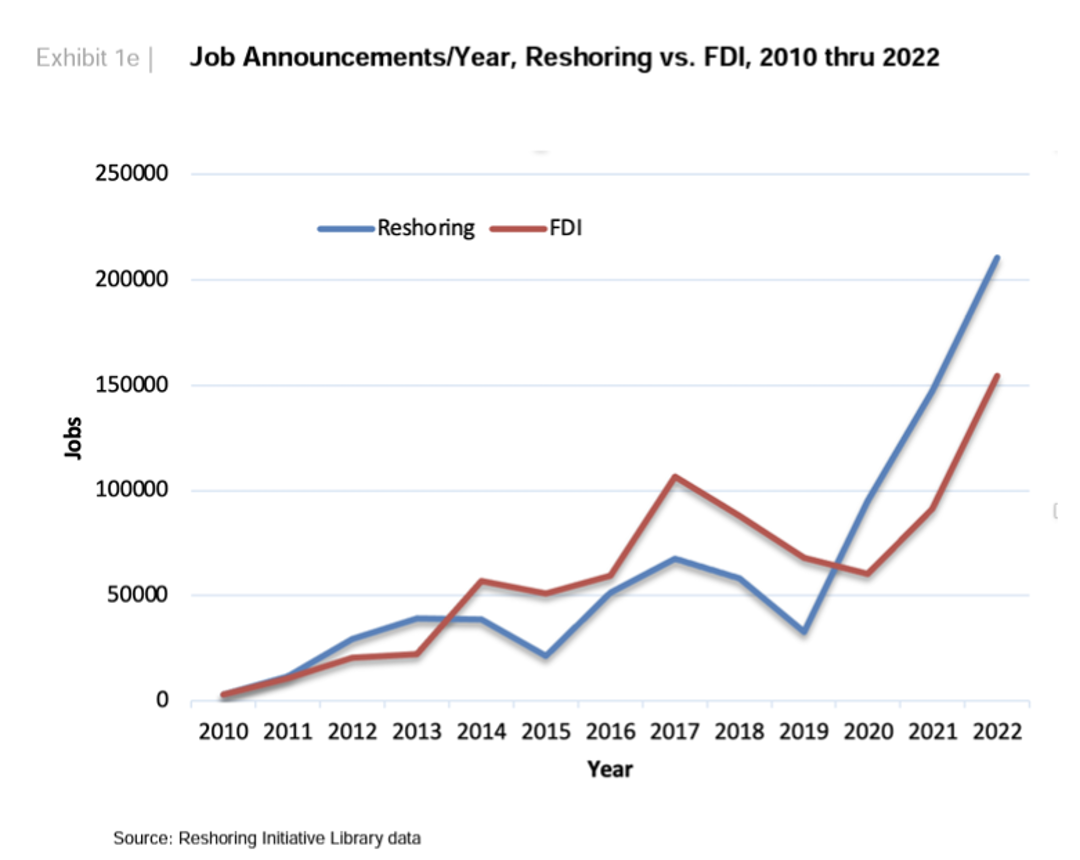
Onshoring not only addresses supply chain challenges but also creates opportunities for new jobs, economic growth, and increased exports for the United States. In 2021, onshoring and manufacturing created 261,000 new job opportunities for U.S. citizens, and this trend continued with 350,000 new jobs in 2022, representing a 34% year-over-year increase (see chart below). Self-reliance is another factor driving onshoring. The U.S. has been grappling with trade and budget deficits, but recent improvements suggest a positive trajectory. March 2023 exports were $256.2 billion, contributing to a slight economic recovery. Year-to-date, the goods and services deficit decreased $77.6 billion, or 27.6%, from the same period in 2022. Exports increased $61.4 billion or 8.7%. Onshoring presents an opportunity to stimulate internal spending and enables new employees to contribute their wages to the U.S. economy.
The Movement to Bring Manufacturing Back
The convergence of robotics, supply chain optimization, and a growing focus on manufacturing efficiency has fueled a compelling movement to bring manufacturing back to the U.S. and neighboring countries through onshoring strategies. This transformation holds significant promise as it addresses economic challenges, spurs job creation, and enhances the country’s logistical capabilities. By embracing automation, optimizing supply chains, and investing in local manufacturing, the U.S. is positioning itself for a resilient and prosperous future.

 Jay Flynn
Jay Flynn
 Baily Datres
Baily Datres Mike Otillio
Mike Otillio
 Jesse Tollison
Jesse Tollison
 Patrich Jett
Patrich Jett