Nearshoring manufacturing to Mexico has become a compelling trend, fueled by factors like proximity to the U.S. market, cost advantages, favorable trade agreements, and a skilled workforce. Mexico offers geographical and time-zone benefits, making it an attractive option for businesses seeking operational improvement. The U.S. border region and Monterrey have emerged as key nearshoring hubs, attracting companies across industries. In this blog post, we’ll explore the driving forces behind Mexico’s nearshoring trend, featuring insights from Colliers experts and examining its impact on the manufacturing landscape.
Nearshoring first began with the maquiladora program in the mid-1960s, followed by waves in 1994 with NAFTA (now USMCA) and in 2020 due to global supply chain disruptions and U.S.-China import taxes. Below are some of the major factors driving the recent nearshoring trend in the region.
Proximity to the U.S. Market
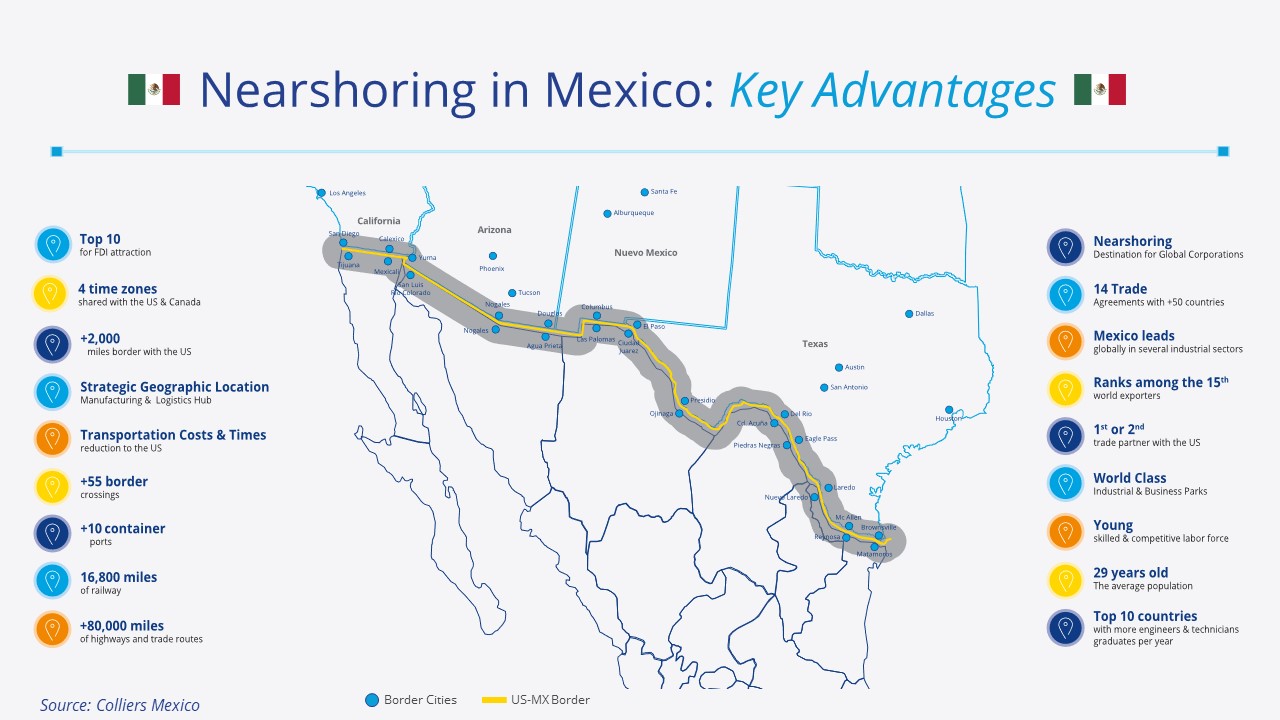
Mexico’s strategic location adjacent to the U.S., the world’s largest consumer market, serves as a magnet for companies looking to establish manufacturing operations. Proximity reduces production-to-consumer time, outperforming Asian competitors with longer shipping times. This advantage not only ensures quicker and more efficient delivery but also enhances customer satisfaction and enables businesses to swiftly respond to changing market demands.
With 55+ border crossings along the 2,000-mile U.S.-Mexico border, products reach U.S. customers in 3-5 days. E-commerce further accelerates delivery, bolstering Mexico’s competitive advantage. A noteworthy trade hub, the Laredo, Texas border crossing stands out as a critical gateway, handling over 30% of all imports into the U.S.
Duty Free and Value Added Tax Incentives
Under the USMCA Trade Agreement, qualified products can benefit from duty-free and value-added tax incentives.Rich Kwasny, a Senior Vice President at Colliers, recently shared how these incentives enable goods to be imported into the U.S. from Mexico without incurring duties or taxes, boosting cost-efficiency and enhancing supply chain agility. “With the USMCA Trade agreement, many foreign manufacturers are able to ship their goods or raw materials to Mexico via the Port of Long Beach/Los Angeles duty-free, complete assembly or package their product in Mexico, then export their product duty-free to the U.S.,” said Kwasny. “Lately, this has been one of the most important factors for companies seeking to move manufacturing operations to Mexico.”
Another Colliers expert in the region, Sergio Resendez, also commented with his experience. “The automotive sector stands at the forefront of companies driving the nearshoring trend in Mexico. With the implementation of new rules under the USMCA, which mandates that 75% of automotive parts be produced within the North America region, companies are strategically leveraging Mexico’s manufacturing capabilities. Beyond automotive, other sectors such as appliances, plastics, and metal mechanics are also witnessing remarkable activity in the Mexican market.”
The Mexican automotive industry is at the forefront of global EV mobility transformation, attracting projects such as Tesla’s nearshoring announcement. By 2026-2027, estimates project Mexican automotive production to reach 5 million vehicles, with around 20% being EVs.
Geopolitical Considerations
Geopolitical tensions have also influenced companies’ decisions to seek alternative manufacturing locations. The uncertainty surrounding trade relationships, tariffs, and intellectual property concerns has led to an increased number of overseas companies exploring Mexico as a viable option to mitigate risks. By shifting their manufacturing operations to Mexico, these companies can reduce their exposure to geopolitical uncertainties and maintain proximity to the North American market.
Evolving Mexican Labor Force
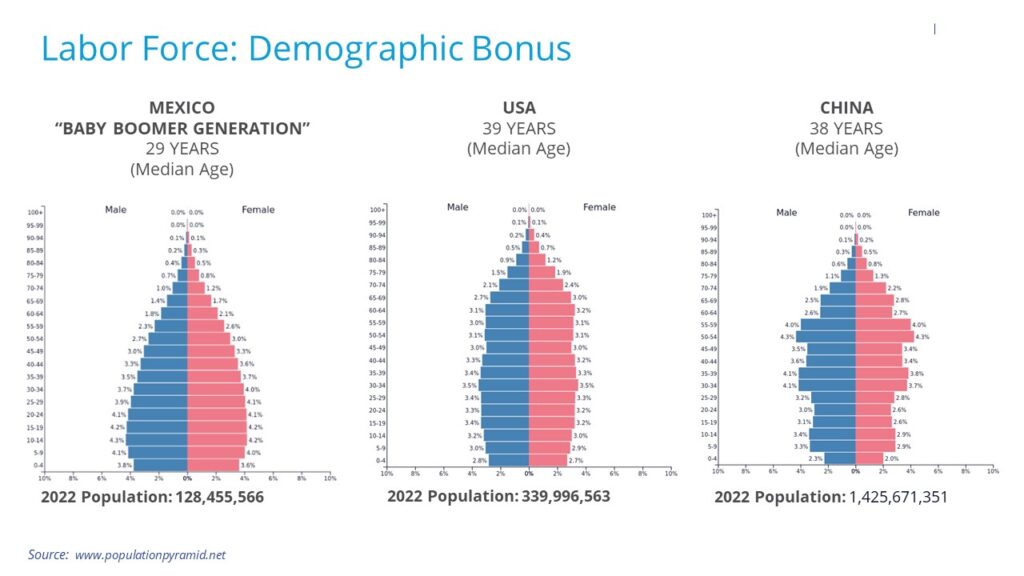
Mexico’s labor force has undergone a remarkable transformation, expanding from low-cost assembly to diverse industries like automotive, aerospace, and high-tech manufacturing. Skilled workers and competitive wages make Mexico an attractive choice for companies expanding their operations. The country’s educational system, technical training programs, and English proficiency contribute to a skilled workforce that meets industry demands. With a youthful average age of 29, Mexico’s talent pool is increasingly sought after as U.S. baby boomers retire. Check out the graphs below for a visual comparison of the demographic differences between the U.S., China, and Mexico.
Lease vs. Own and Spec vs. Build-to-Suit
While most companies prefer leasing facilities in Mexico, Asian companies tend to lean towards purchasing properties. According to an article from earlier this year in Mexico Daily Post, a group of investors from China, Taiwan, Japan and South Korea recently pulled 44 factories, production lines and distribution centers from Asia to relocate and install them in Monterrey, Saltillo, Mexico City, Tijuana, Ciudad Juárez and Guadalajara.
Existing spec buildings are popular due to their faster availability, while build-to-suit options cater to the specific needs of complex manufacturing processes. This flexibility in real estate options allows companies to align their facility choices with their business objectives, whether it’s testing the market or establishing long-term operations. Sergio Resendez shared his perspective, noting “North American and European companies tend to lean towards leasing options, while their Asian counterparts often prefer to purchase properties outright.”
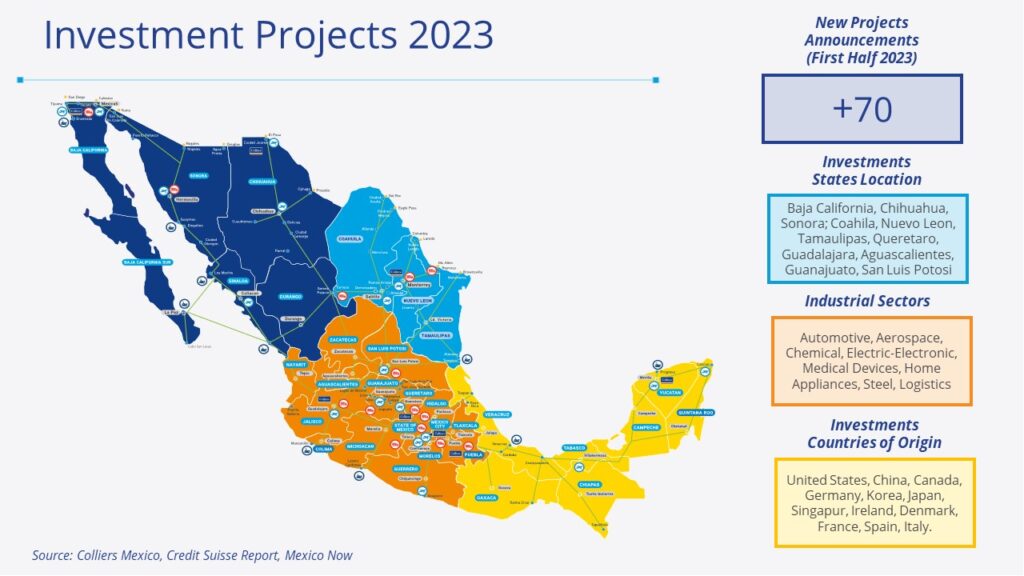
Unveiling the Nearshoring Impact: Mapping the Regions and Global Corporations in Mexico
Below is a preview visual to a map that showcases the regions and global corporations impacted by nearshoring in Mexico. Over the last 23 years, the map has been continuously updated to align with the ever-changing economy and dynamic requirements, especially in the post-pandemic era. Mexico, leveraging its strategic advantages, stands poised to redefine the global manufacturing landscape, empowering companies with a distinct competitive edge and propelling economic prosperity throughout the region.

 Rafael McCadden
Rafael McCadden
 Baily Datres
Baily Datres Mike Otillio
Mike Otillio
 Jesse Tollison
Jesse Tollison
 Patrich Jett
Patrich Jett